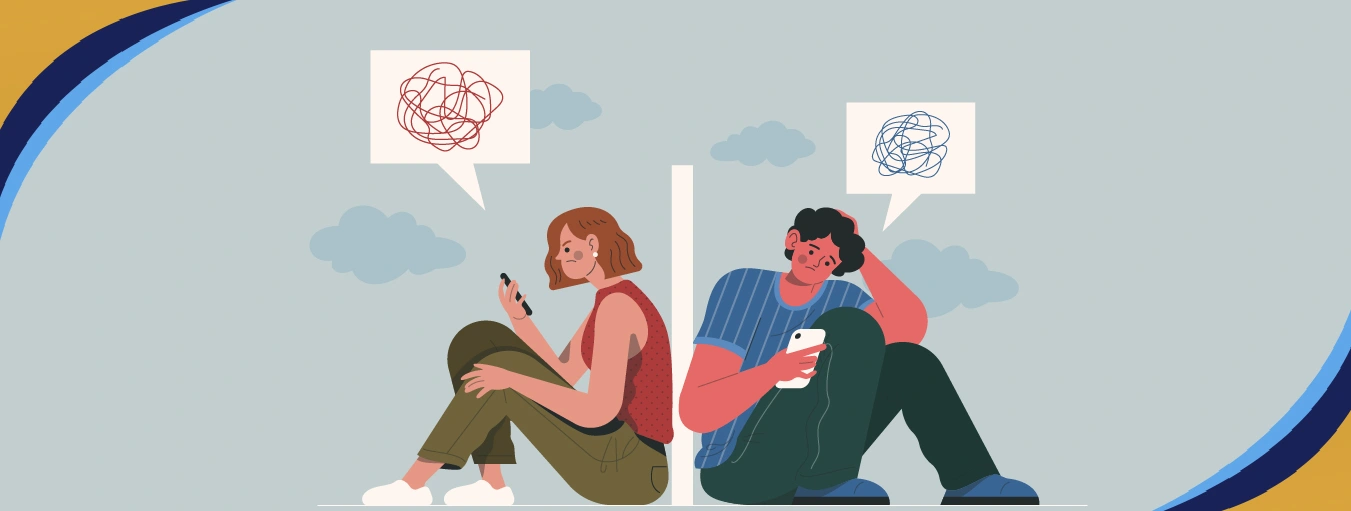
Impulsively, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) manifests itself in several forms, and some lead the sufferer to experience extreme confusion and distress. Of all the forms of OCD, the “groinal response” seems to be among the most poorly understood. This term refers to the physical discomforts that a person may feel in the genital area, usually due to intrusive thoughts of a sexist type. But people who learn about it can develop anxiety, guilt, and confusion whenever the groinal response is elicited.
Thus, this blog is written to help readers understand the groinal response, how to stop groinal response OCD, how it is connected to OCD, and how it can be best dealt with.
What Is OCD’s Groinal Response?
The groinal response in OCD can be defined as a tickle or other physical feeling in the genital region when a person has obsessions and when these are of a sexual kind. It has a sensation similar to tingling, tightness, or even arousal, but not the arousal that people commonly think of. However, it is a bodily manifestation triggered by either anxiety or excessive concentration on the area.
For OCD sufferers, especially those with sexual compulsions and sexual obsessions, the groinal response can very much be distressing. They may be wondering why their body reacts in that manner to thoughts that they consider disgusting, improper, or sinful. This physical reaction is what might put the individual into a cycle of obsession and compulsion because they may attempt to engage in other mental or physical behaviors to “test” whether they are aroused.
Read More: Do You Ever Wonder That Your OCD Thoughts Are Not Real?
The Cycle Of OCD And Groinal Response
Before we define the groinal response, it is critical to understand something about OCD and how it operates. OCD is defined by the presence of ideas or impulses the patient cannot control (obsessions) and the actions or mental behaviors utilized to neutralize or diminish the distress triggered by these ideas (compulsions). For instance, in groinal response, an individual experiences a thought about something sexually forbidden or unethical, such as having a sexual thought about a relative or a child. This is an unwanted thought and results in anxiety. In return, the person becomes overly concerned with any sensation in their genital region.
The way anxiety manifests itself is distressing, or it can be referred to as the physical reaction to anxiety. Stress raises the heart rate and the production of sweat and muscle contraction. In particular, obsessive-compulsive disorder symptoms for those who experience physical anxiety can be observed throughout the genital area in cases when their feeling can be compared to sexual arousal only because it is, in fact, the body’s reaction to stress. However, because such a sensation occurs in response to sexual thought, the OCD-stricken individual may start worrying that such a sensation signifies something, for instance, a sexual interest in the thought, or that an individual is a bad person for entertaining the thought at all.

Why Does The Groinal Response Cause Anxiety?
Whereas for a non- OCD person, an intrusive thought is usually brief and can be brushed away as having been just a momentary weird thought that had crossed the mind. Nonetheless, for a patient with OCD, particularly sexual OCD (also regarded as pure OCD), the groinal response turns out to be the relevant object of their growing concern and anxiety. They may start questioning:
- “Why should I have this sexually inclined urge?”
- Of this, I wonder, do I have a sexual preference for something off base?
- What people should say to me, “You are bad or immoral.”
These thoughts can be anxious, but they are worth remembering. Patients with OCD tend to react to the groinal response, meaning that some of their obsessive thoughts have a real or significant meaning, which they do not. This is a typical groinal response of the body to stress; however, when the body gives this response, it is misconstrued to worsen the OCD symptoms. The person may become preoccupied with the genital area to determine whether the aversive feeling recurs to ensure that the groinal response is not elicited by thinking about it.
Read More: Is Social Anxiety Disorder A Disability?
Misconceptions About OCD And Groinal Response
Among the worst things that people with OCD associate the groinal response with is the belief that it holds significance as to their desires, morality, or identity. This means that the groinal response is not indicative of genuine sexual interest or, more specifically, sexual predatory intent. It is an automatic and stress-invoked response that exists in the physiological levels of bodily structure and can be accumulated by a particular perception of one’s physical condition. As easily as a person can blush when embarrassed or feel a knot in the stomach stress, the groinal response is just as natural, being a physical manifestation of the mind focusing on a distasteful thought.
Furthermore, it is important to recognize that these obsessions are not the patient’s wants and needs or things they overlook. Intrusive thoughts are peracute, unpleasant, and persistent, and these features are characteristic of OCD. They are not real, even though the OCD sufferer may genuinely feel that way at the time that they are saying them.
How To Manage OCD Groinal Response
The groinal response in OCD should be dealt with as any bodily sensation one gets when anxious and at the same time tackle the OCD properly. Here are several approaches that can help:
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
CBT has been specifically identified, in a particular variant known as Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP), as the best available treatment approach for OCD. In ERP, the individual is exposed little by little to the stimuli that cause the thoughts without being able to perform the compulsion. For the individual with a groinal response, it might entail sitting with the anxiety of the sensation without the need to check, test, or attempt to cancel out the thought.
For example, the therapist may suggest the individual recall one successful intrusive thought and not perform the relevant check for groinal sensations. In time, this leads to less anxiety around the thought and assists the person in recognizing that the groinal response is not indicative of something greater.
- Mindfulness and Acceptance
Mindfulness is similar to being aware of the thoughts being pondered on and the physical feelings with no criticism. Awareness strategies may be applied if a person feels a groinal response so that the person learns to operate with it without labeling it as something significant. The issue here is simply to allow the sensation to be and to endure the experience without seeking to analyze why such a reaction is being felt or what message the body is conveying.
In particular, acceptance should be used as a way to decrease the influence of intrusive thoughts and physical sensations in people’s lives. Instead, they read about or discuss compulsions to try to stop the sensation, but they are encouraged to let it be, knowing that it will diminish of its own accord.
- Education
Knowing the nature of OCD as well as the groinal response is critical to preventing increased anxiety. Education assists people with OCD to gain knowledge that intrusive thoughts as well as groinal responses are signs of OCD and do not represent their wishes or immoral personalities. Often, the sufferer feels alone and ashamed or guilty, which can be alleviated by realizing that thousands of other men experience the same thing.
- Medication
Sometimes, medications can control symptoms of OCD and, therefore, the groinal response as well. Antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a type of drug that can be taken to control serotonin levels in the brain and help decrease the incidences of the framing of obsessive thoughts and physical manifestation of anxiety. Moreover, it treats the depression signs as well.
- Self-Compassion
Managing the groinal response in OCD is emotionally draining. People must be kind to themselves and remember that people suffer from these signs. Self-compassion and gentle self-criticism are anathema to recovery and can harm one’s well-being.
Read More: Which Brain Region Is Believed to Play a Critical Role in OCD?
Male Perspective On The Groinal Response
In men, there is yet another problem referring to the so-called groinal response, which can be worrying because it is directly connected with physical arousal, which is easy to diagnose. Males might have feelings like tickling in the area, it getting hard at times, though not as hard as when a man is sexually attracted to a woman; this causes immediate reactions about whether what one is experiencing is sexual attraction towards the thoughts that are harassing him. For instance, common male intrusive thoughts may include thoughts about children, family members, groinal responses, or even violent sexual content, thereby worsening common distress indicators among the sufferers.
Common Fears for Men:
- Fear of Sexual Attraction: Men may become almost panicked over the groinal response for the reason that it reveals that they are sexually interested in the improper or repulsive content of the intrusive thoughts.
- Erectile Response: Again, due to physical arousal response being generally more visually demonstrable in males (erections, etc.), men may mistakenly attribute their slightest discomfort or breathlessness, especially, to feelings of arousal when it is indeed anxiety.
- Shame and Guilt: Because of the negative appraisals, men may experience profound shame or guilt with regards to having compulsive sexual thoughts and belief that groinal response is indicative of moral character or desire.
- Hyperawareness: One can find that males with OCD may develop very sensitive to changes in their genital region, and they are obsessed with checking for signs of hardness, which reinforces their obsession with the feeling.
Female Perspective On The Groinal Response
In women, the groinal response can be described as having sensations such as tingly, hot, or sensitive in their genitals. When everything comes to sexual topics, women can have Obsessive Compulsive Disorder and think about children, members of the family, and different situations that are opposite to their beliefs. Like men, they may mistakenly understand the groinal response as a signal that they are somehow sexually aroused by these thoughts, which would make them feel incredibly guilty and anxious.
Common Fears for Women:
- Misinterpreted Sensations: This means that it is still difficult for women to differentiate between the groinal response from other bodily experiences such as vaginal wetness or heat, which are not always associated with sexual arousal, yet they increase social anxiety if encountered during maintenance intrusive thoughts.
- Fear of Being “Bad”: Women can feel as if the groinal response means that there is something inherently bad about them as a person, which will cause increased feelings of guilt if it goes against one’s personal or religious morality.
- Body-Related Intrusions: Some women may develop themes of sexual assault or fears of being attacked, and the groinal response may be particularly aversive in such circumstances, as the body seems to be sexually aroused by situations that are frightening towards the woman.
- Less Visible Physical Response: Sexual arousal in women is not as observable as that in men most of the time. This can confuse women as they tend to fail to distinguish between normal body feelings and that of the ocd groinal response checking regarded as an outcome of OCD.
Read More: Generalized anxiety vs panic disorder: A Closer Look
Wrap Up!
Thus, the groinal response OCD is an under-appreciated and uncomfortable motor phenomenon associated with the compulsive themes that result in worry, shame, and uncertainty in those experiencing the compulsions. Men may construct these feelings as a form of pornographic stimulation, and women may interpret them as predatory advances of being harassed, Increased concern, and preoccupation. However, one must know that the groinal response is induced by stress and that it has no say in one’s preference or morality. However, if treated appropriately, the subjects in this study can control such symptoms when receiving CBT, mindfulness, and self-compassion exercises, and their distress levels should decrease over time. If you desire to learn more about OCD groinal response, then now is the right time to contact the telehealth services of Orange Coast Psychiatry.